AISI 4130 Alloy Steel
AISI/SAE 4130 steel grade is a versatile alloy with good atmospheric corrosion resistance and reasonable strength up to around 315º C (600º F). It shows good overall combinations of strength, toughness and fatigue strength.
Supplying Size:
Rolled: Diameter 40-200mm
Forged: Diameter 80-600mm
AISI 4130 Steel Specification and Relevant Standards
| Country | USA | BS | BS | Japan |
| Standard | ASTM A29 | EN 10250/EN10083 | BS 970 | JIS G4105 |
| Grades | 4130 | 25CrMo4/1.7218 | 708A25/708M25 | SCM430 |
ASTM 4130 Steels And Equilvalents Chemical Composition
| Standard | Grade | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Mo |
| ASTM A29 | 4130 | 0.28-0.33 | 0.40-0.60 | 0.035 | 0.040 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.15-0.25 |
| EN10250 /EN10083 |
25CrMo4/ 1.7218 |
0.22-0.29 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.025 | 0.035 | ≦0.40 | 0.90-1.2 | 0.15-0.30 |
| JIS G4105 | SCM430/ SCM2 |
0.28-0.33 | 0.60-0.85 | 0.030 | 0.030 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.90-1.2 | 0.15-0.30 |
AISI 4130 Steel Mechanical Properties
| Properties | Metric |
| Tensile strength, ultimate | 560 MPa |
| Tensile strength, yield | 460 MPa |
| Modulus of elasticity | 190-210 GPa |
| Bulk modulus (Typical for steel) | 140 GPa |
| Shear modulus (Typical for steel) | 80 GPa |
| Poissons ratio | 0.27-0.30 |
| Elongation at break (in 50 mm) | 21.50% |
| Reduction of area | 59.6 |
| Hardness, Brinell | 217 |
| Hardness, Knoop (Converted from Brinell hardness) | 240 |
| Hardness, Rockwell B (Converted from Brinell hardness) | 95 |
| Hardness, Rockwell C (Converted from Brinell hardness, value below normal HRC range, for comparison purposes only.) | 17 |
| Hardness, Vickers (Converted from Brinell hardness) | 228 |
| Machinability (Annealed and cold drawn. Based on 100% machinability for AISI 1212 steel.) | 70 |
Thermal Properties
| Properties | Metric |
| Thermal conductivity (100°C) | 42.7 W/mK |
Smelting Option
1 EAF: Electric Arc Furnace
2 EAF+LF+VD: Refined-smelting and vacuum degassing
Forming Option
1 Hot rolling process
2 Hot Forging: Electro-hydraulic; High-speed-hydraulic; Oil-hydraulic; Precision-forging
Heat-treatment Option
1 +A: Annealed (full/soft/spheroidizing)
2 +N: Normalized
3 +NT: Normalized and tempered
4 +QT: Quenched and tempered (water/oil)
Suface Option
1 Black Surface
2 Grounded: Bright but rough ; Not precision
3 Machining for plate: Bright and precision; Little turning scar
4 Peeled/Turned: Bright and precision; Little turning scar
5 Polished: Very Bright and precision size; Not turning scar
Other Services
1 Cutting: Small pieces
2 CNC Machine: Produce as your drawing
3 Package: Bare/Nylon/Canvas/Wooden
4 Payment:T/T, L/C, O/A(request credit)
5 Transport:FOB/CFR/CIF/DDU/DDP (train/ship/Air)
Forging of 4130 Alloy Steel
ASTM A29 Grade 4130 steel should be forged between 1230 and 950 º C (2250 and 1750 º F). The lower the finishing temperature from forging, the finer will be the grain size. If the 4130 alloy steel is forged at too low a temperature, there is a risk of the formation of a non-uniform structure in certain areas of the forged part, necessitating a normalizing treatment, prior to further heat treatment.
What is 4130 steel?
AISI 4130 alloy steel is a medium carbon, low alloy steel in ASTM A29 standard. ASTM 4140 steel is also commonly referred to as a chromoly steel, or chrome moly steel, containing nominally 0.28-0.33% Carbon, 0.8-1.1% Chromium and 0.15-0.25% Molybdenum. It is similar to 4140 steel which has a higher carbon level (0.28-0.33%), giving 4130 material improved weldability, at the expense of through thickness strength. With the proper heat treatment it is also readily machined. Annealing ASTM 4130 alloy steel offers excellent ductility. AISI 4130 steel is usually supplied as round bar commonly in the hardened and tempered condition.
Annealing of 4130 steels
Annealing of 4130 steel forgings may be carried out by transferring the part straight from the forging operation to a furnace held at a suitable temperature, around 860º C (1575 º F) for annealing, holding for a suitable time then furnace cooling. In this way a structure suitable for machining may be obtained. This treatment is best used for parts with simple shapes. If the 4130 forging is such that some sections will finish much colder than others then a uniform structure will not be obtained and for best results a spheroidizing anneal at around 750 º C (1380 º F) may be used. It is safe to say that experience alone will decide the best type of annealing treatment to be used prior to machining. It should then be cooled in the furnace at a rate of less than 50 F per hour down to 900 F, followed by air cooling from 900 F.
Normalizing of Alloy Steel 4130
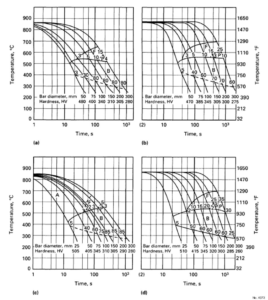
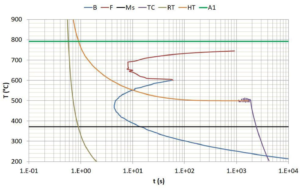
The nominal normalizing temperature for 4130 is 900 º C (1650 º F) followed by the 1600 F soak and oil quench, but production experience may necessitate a temperature either 50 º F (10 º C) above or below this figure. In fact when forgings are normalized before, for example, carburizing or hardening and tempering, the upper range of normalizing temperatures is used. When normalizing is the final heat treatment, the lower temperature range is used.
Hardening of AISI 4130 Alloy Steel
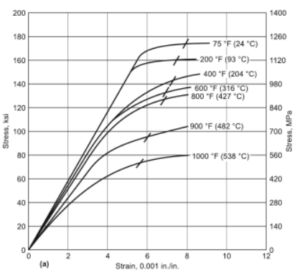
The steel 4130 should be austenitized – i.e. all micro constituents transformed to austenite – at 1500 to 1600 º F (815 to 870 º C). The actual austenitizing temperature is a function of chemical composition within the analysis range, section size and cooling method. Smaller sections of 4130 might be quenched in oil, heavier sections in water.
Tempering of 4130 Steel
The actual tempering temperature will depend on what required properties are needed. Alloy steel 4130 is tempered at between 398 ºC -565 ºC (750 F and 1050 F), depending upon the strength level desired. The lower the tempering temperature the greater the strength. However, tempering should not be carried out between 200 – 420 ºC (400 – 790 º F) to avoid the danger of embrittlement.
Machinability
The AISI 4130 alloy is readily machinable by conventional methods. Simple shapes might be machined following a normalizing treatment, whereas more complex shapes will require annealing. However, machining becomes difficult when the hardness of the 4130 steel is increased.
Welding
AISI 4130 steel is also good in weldability, and the 4130 alloy may be welded by any commercial method. The material may require a post-weld stress relief heat treatment in certain instances.
Low-hydrogen electrodes are recommended together with preheat at 150 – 260 º C (300 – 500 º F) to be maintained during welding, Cool slowly and stress relieve where possible.
Application of 4130 Steel
AISI 4130 steel alloy is used primarily in the construction of commercial and military aircraft and ground support systems. Alloy steel 4130 is an intermediate strength material. Lighter gauges offer lighter weight but still maintain great strength, making it excellent for auto racing and aerospace. This low alloy 4130 steel is widely used in many applications, and some typical application areas are as follows:
Commercial aircraft, aircraft engine mounts
Military aircraft
Automotive
Machine tools
Hydraulic tools
Auto racing
Aerospace
Oil and gas industries – as forged valve bodies and pumps
Agricultural and defense industries etc.
Alloy steels are designated by AISI four-digit numbers. They are more responsive to mechanical and heat treatments than carbon steels. They comprise different types of steels with compositions which exceed the limitations of B, C, Mn, Mo, Ni, Si, Cr, and Va in the carbon steels.
AISI 4130 alloy steel contains chromium and molybdenum as strengthening agents. It has low carbon content, and can be welded easily. The datasheet below provides further detail.
Other Designations
Other designations that are equivalent to AISI 4130 alloy steel include the following;
| AMS 6348 | AMS 6371 | ASTM A331 | ASTM A829 | DIN 1.7218 |
| AMS 6350 | AMS 6373 | ASTM A506 | MIL S-18729 | UNI 25 CrMo 4 |
| AMS 6351 | AMS 6374 | ASTM A507 | MIL S-6758 | JIS SCCrM 1 |
| AMS 6360 | AMS 6528 | ASTM A513 | SAE J1397 | JIS SCM 2 |
| AMS 6361 | AMS 7496 | ASTM A519 | SAE J404 | SS 2225 |
| AMS 6362 | ASTM A29 | ASTM A646 | SAE J412 | B.S. CDS 110 |
| AMS 6370 | ASTM A322 | ASTM A752 | AFNOR 25 CD 4 (S) | SAE J770 |